Thomas Crease and the Custis Square Garden Layout

Illustration of the garden at Seavenhampton in the early 18th century.
Colonial Williamsburg’s archaeologists have made important recent discoveries to help us reconstruct the layout of John Custis IV’s early eighteenth-century garden.
When Custis first began laying out his garden in the 1710s or early 1720s, large geometric pleasure gardens were just starting to become fashionable amongst members of the British gentry. For the movers and shakers of early 18th-century English society, laying out ornamental gardens with carefully manicured planting beds and symmetrically aligned shrubs at their country estates was almost as important as collecting artwork to hang in their manor houses. Proper gardening was a way of showing off one’s wealth and taste. Numerous tomes were published describing the correct geometric angles and ratios, often derived from classical Roman and Greek architecture, for gentlemen gardeners to use when designing their gardens.
While some of these gardeners wrote extensively about their garden layouts, Custis’ surviving letters rarely mention the subject. The main focus of Custis’ letters is the plants themselves and the appropriate way of growing them, not how they should be placed in his garden. Therefore, one of the questions archaeologists set out to answer during excavations was how exactly the gardens at Custis Square were laid out.
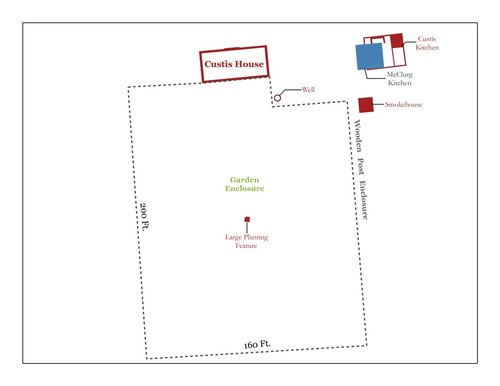
Figure 2: Map of Custis Square with enclosure and central planting marked.
Through recent research, we have been able to determine that, soon after Custis finished building the large brick house at Custis Square circa 1715, he had a large wooden fence constructed around a 160-foot by 200-foot enclosure directly behind the manor. Once we confirmed the dimensions of this garden enclosure, we decided to dig directly in the center to see if there was anything to mark the middle of the garden.
Lo and behold, we found a large planting hole! This feature was larger than any other garden planting we have found so far and was placed exactly in the center of the enclosure. It appears that Custis’ garden was laid out in a fashionable geometric pattern centered around a large tree or shrub located in the center of the garden enclosure (Fig. 2).
Figure 3: Thomas Crease residence on Duke of Gloucester Street.
While many English aristocrats got inspiration for their garden layouts from books, it became more and more common over the course of the eighteenth century to hire a professional gardener when designing an ornamental garden. These men would help landowners design and construct their gardens, procure plants from greenhouses, and coordinate the pruning, watering, and maintenance required to keep the garden in good shape.
While we have plenty of documentary evidence that Custis purchased his own plants and ordered his enslaved laborers to maintain his garden, it is quite possible that he hired a gardener to help design his garden. If so, Custis most likely acquired the services of a man named Thomas Crease, his neighbor and the only professional gardener known to have resided in Williamsburg in the early eighteenth century.
We don’t yet know where Thomas Crease was born or where he received his training, but we do know that he was in Virginia and working as a gardener at William Byrd II’s plantation at Westover by the second decade of the eighteenth century. By the time William Byrd II returned to Virginia from England in February 1720, Crease had left his service and was living in Williamsburg. However, Crease visited Westover several times to help plan an extension to the garden, and one time he brought a letter with him from Byrd’s brother-in-law, who was... you guessed it… John Custis IV!
Thomas Crease lived on Lot 352 in Williamsburg, less than a block from Custis Square, for at least 25 years and must have at least known Custis socially since he delivered letters for him. Beginning in 1726, Thomas Crease was hired as a gardener at the College of William and Mary, a position he held until about 1738. Moreover, he did extensive work on the gardens at the Governor’s Palace in the 1720s and 30s.
In addition to working as a gardener, Crease sold plants out of his home. By the time of his death in 1756, his estate was valued at more than 166 pounds, putting him comfortably within Williamsburg’s middle-class residents. While no written documents survive to indicate that Custis hired Crease to design his garden, there is a strong possibility that he at least consulted with the gardener, given the connections between the two men. Indeed, if Custis was not particularly interested in the garden layout, as his writings suggest, then the geometric patterns that we are beginning to uncover in the soil may have begun as the brainchild of Thomas Crease.




